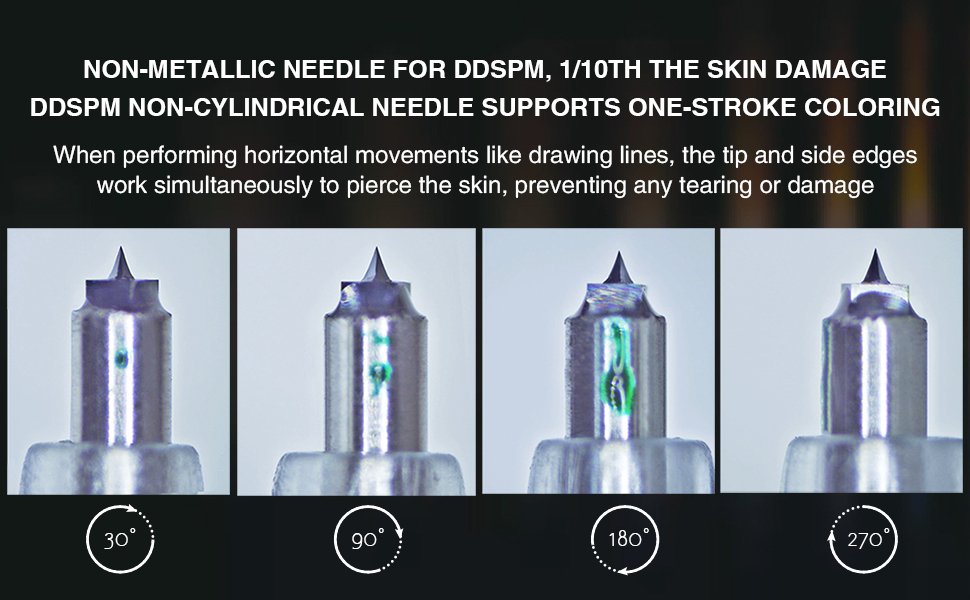
Polyhedral Structure
Platinum diamond needle tips are composed of multiple facets, with pointed fronts and angular sides. During lateral movement, these edges puncture the skin, allowing for precise coloring with minimal damage. Metal needle tips, on the other hand, are cylindrical with iron pillars on all sides. Consequently, regardless of the technique used, lateral movement inevitably tears the skin, resulting in greater damage.
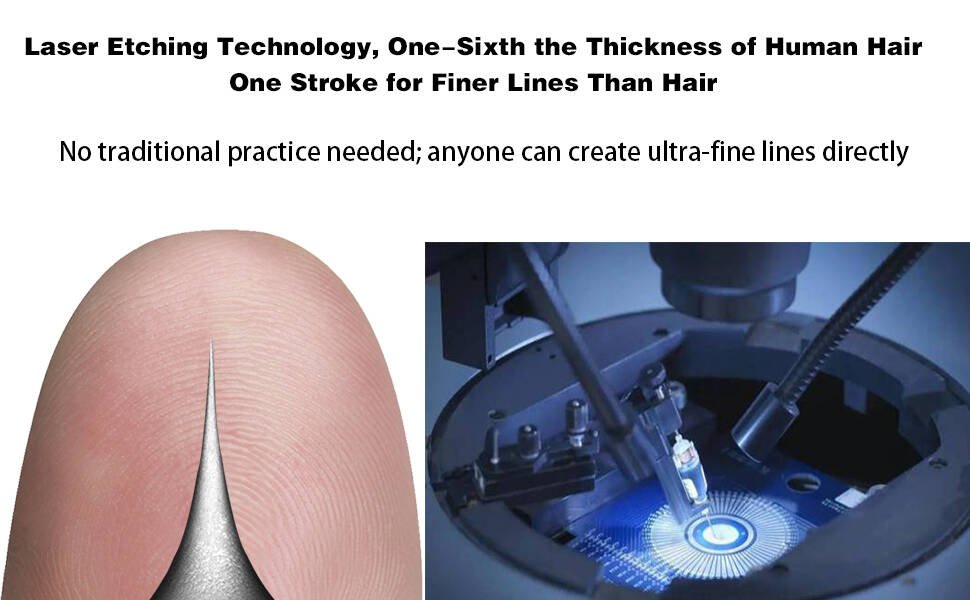
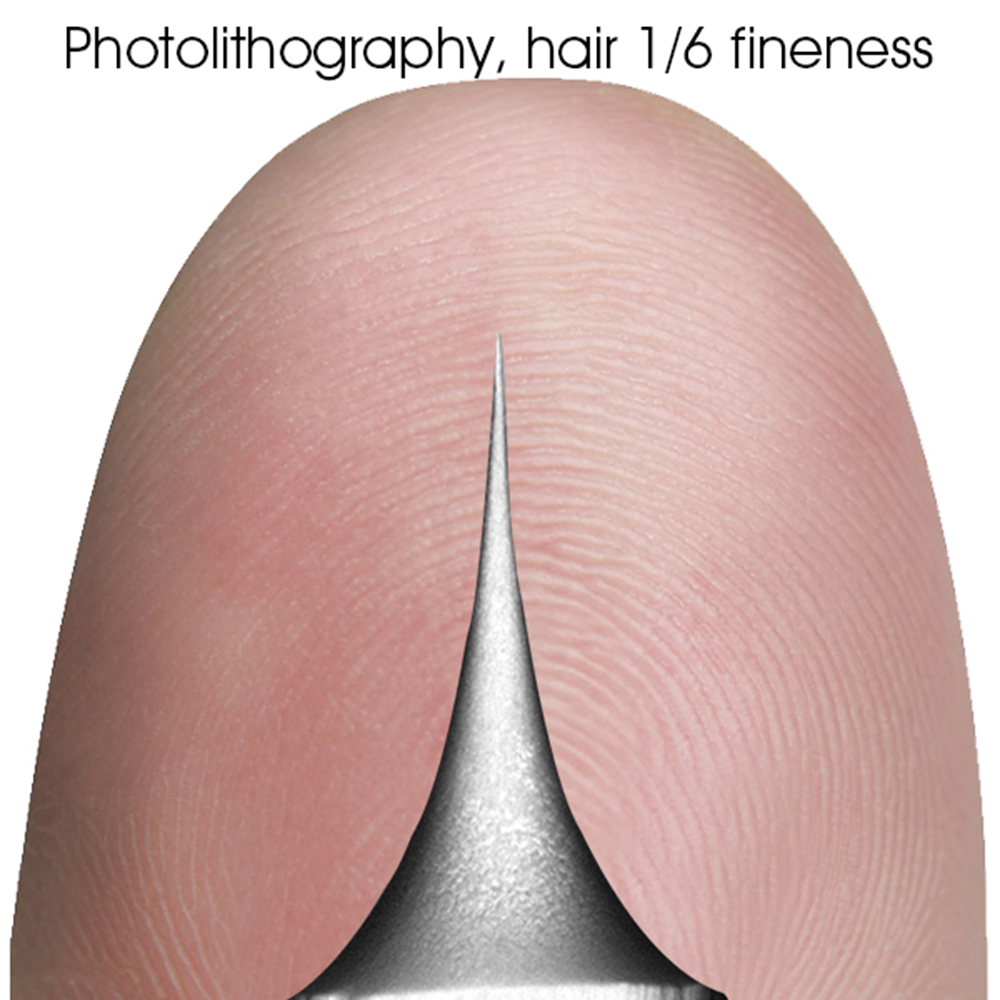
Needle tip lithography process
Platinum diamond tips are made using lithography process, achieving a fineness of 1/6 of a hair strand. Metal needle tips, made by grinding with sandpaper, have limited precision and are therefore comparatively blunt.
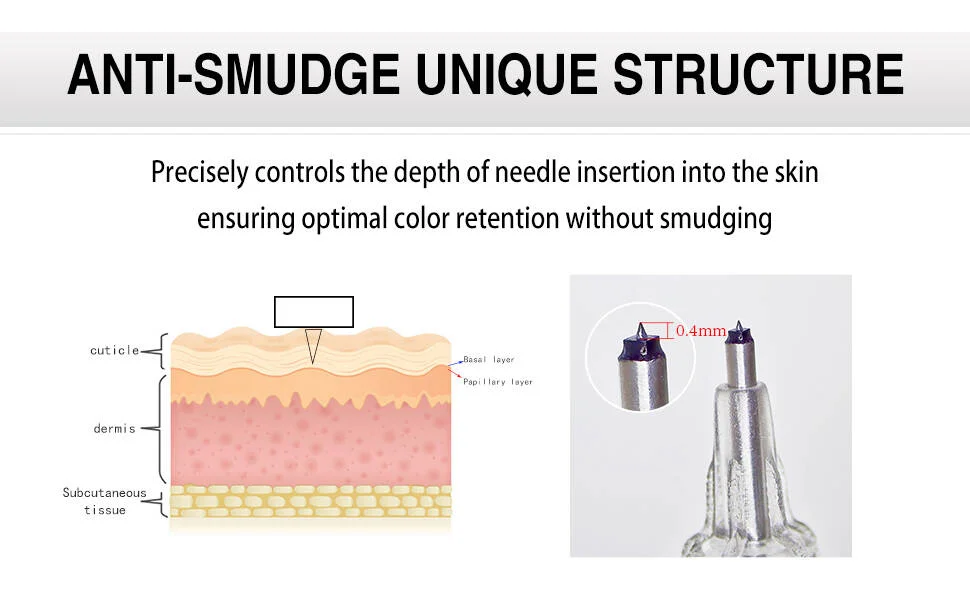
Anti-Smudging Base Structure
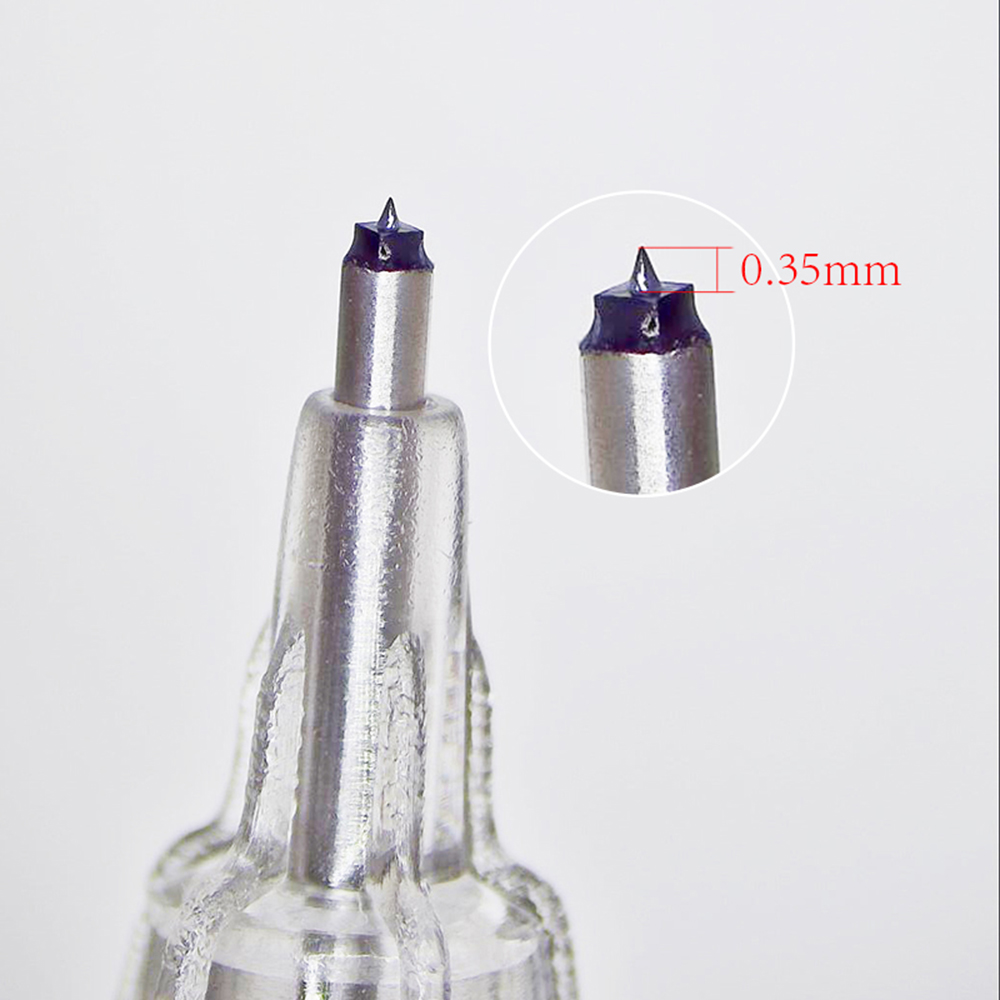
Underneath the platinum diamond needle tip lies an anti-smudging base structure, precisely controlling the penetration depth to 0.35mm, placing the color in the optimal layer for retention and coloring.
By innovating materials, techniques, and structure, skin damage is reduced to one-tenth of metal needles, achieving a tenfold color retention efficiency.


Non-metallic material
The Mohs hardness coefficient of metal is 4-5, so metal needles tend to soften. They deform during machine movement, especially during lateral stretching, affecting operational precision and increasing ineffective skin damage. The Mohs coefficient of platinum diamond is 10, so even finer platinum diamonds do not soften or deform.
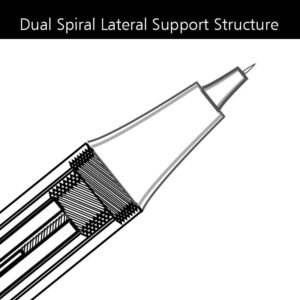
Dual Spiral Lateral Support Structure
The platinum diamond device employs a dual-lock design with two interlocking locks. When the needle tip moves laterally, it constrains ineffective swinging displacement. Tested by Kapok, the swinging amplitude is <3%, demonstrating significantly higher stability compared to traditional machine interfaces

Integrated Dotting Head Innovation
The dotting head (electric graphite core pen) is installed on the machine head just like the machine needle head. After turning on the machine, you can learn paper lines in motion. This replaces the traditional inefficient learning method (using a static pencil during the learning stage, operating the machine, inconsistent hand feel and technique between before and after. This leads to incorrect muscle memory). The dotting head draws on paper and can be replaced with a diamond head for skin operations.
DDSPM vs. Metal Needle Comparison
| Core Metric | DDSPM | Metal Needle |
| Needle Material | Synthetic Diamond | Iron or Steel |
| Needle Tip Fineness | 50-100 Nanometers | Approx. 17 Microns (17,000 Nanometers) |
| Needle Hardness | Mohs Hardness 10, won’t soften | Mohs Hardness 4, softens and deforms |
| Manufacturing Process | Photolithography | Sandstone Grinding |
| Needle Shape | Multi-faceted Cone (including tip and side edges) | Cylindrical (only the needle tip) |
| Skin Piercing Method | Vertical and Horizontal with no skin tearing | Horizontal piercing causes skin tearing |
| Skin Layer Control | Precise color application at 0.35mm layer | Manual control of skin depth required |
| Skin Damage | Minimal skin damage, almost no scabbing | Skin damage is over 10 times more than DDSPM |
| Usage Technique | One-stroke coloring, easy to use | Requires practice with more complex techniques |
| Color Retention Rate | 99% | Low color retention rate |
| Suitable Projects | Spot coloring, stroke coloring | Spot coloring |
| Beginner Learning Curve | Can operate on real skin in 1-3 days | Requires 3-6 months of learning |








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.